When disagreements arise between families and educators or service providers around issues related to the development and implementation of services to address a child's disability, the options for resolution may depend upon if the child is on a 504 plan or an Individualized Education Program (IEP) or Individualized Family Service Plan (IFSP). This could include disagreements over evaluations, eligibility, identification, and placement of children with disabilities.
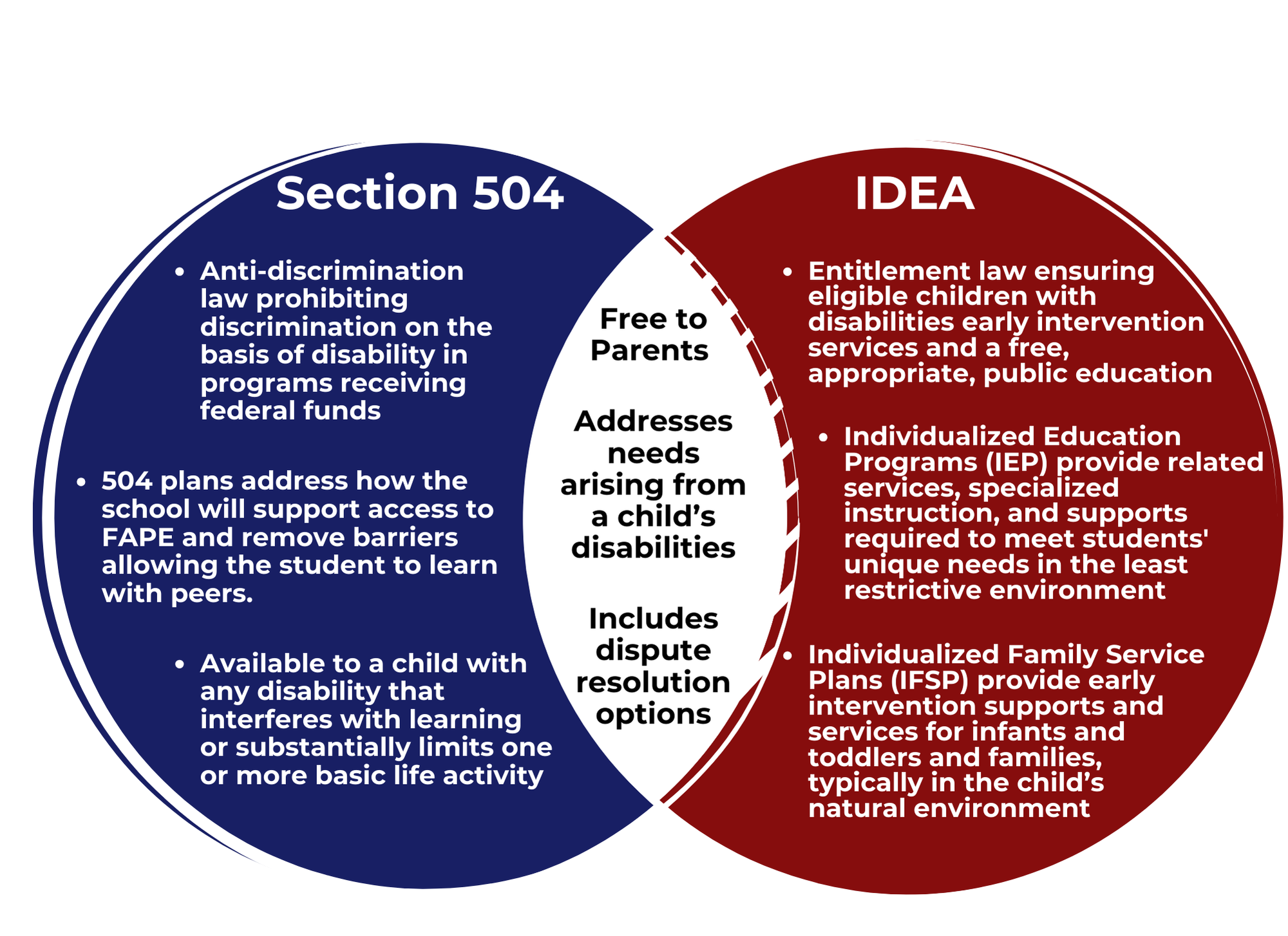
The Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) provides children with disabilities and their parents certain procedural safeguards and rights. These children and their parents are also entitled to protections under two other civil rights laws that prohibit discrimination on the basis of disability - Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973, (Section 504) and Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act (Title II). The Family Education Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA) is another Federal law that provides parents of children with disabilities certain rights related to their children's education. In fact, FERPA protects the privacy of education records of all students.
Please tell us what you think of these resources: Click here to take a short survey.
Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA)
IDEA is a law that makes early intervention services and a free appropriate public education (FAPE) available to eligible children with disabilities throughout the nation. Infants and toddlers, birth through age 2, with disabilities and their families receive early intervention services under IDEA Part C. Children and youth ages 3 through 21 with disabilities receive special education and related services under IDEA Part B.
See CADRE's IDEA Early Intervention Family Guides and Companion Videos (for Part C) and IDEA Dispute Resolution Parent Guides and Companion Videos (for Part B) to find information about the different dispute resolution options available to resolve IDEA-related issues. To access the dispute resolution options available under the IDEA, contact your State Educational Agency or State Lead Agency.
Section 504 of the Rehabilitation Act of 1973
Section 504 is a Federal law that protects the rights of individuals with disabilities in programs and activities that receive Federal financial assistance. Section 504 provides: “No otherwise qualified individual with a disability in the United States . . . shall, solely by reason of her or his disability, be excluded from the participation in, be denied the benefits of, or be subjected to discrimination under any program or activity receiving Federal financial assistance . . . .” Section 504 is designed to guarantee equal opportunity for infants, toddlers, children and youth with disabilities. This includes the right to a free appropriate public education (FAPE). Children with disabilities found eligible under IDEA, Part B and Part C, also have the protections under Section 504, enforceable through the Office for Civil Rights. Information for filing complaints on 504-related issues can be found on the Office for Civil Rights website.
Title II of the Americans with Disabilities Act (Title II of the ADA)
Title II of the ADA prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability by public entities, including state and local agencies, in employment, public services, and accommodations, regardless of receipt of Federal financial assistance. The requirements regarding the provisions of free appropriate public education (FAPE) described in the Section 504 regulations, are incorporated in the general non-discrimination provisions of the Title II regulation. The ADA is intended to assure that individuals with disabilities have access to the same public services as individuals without disabilities.
For education-related discrimination claims, individuals may file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education’s Office for Civil Rights (OCR) which has responsibilities for enforcing Title II. OCR may offer mediation as an alternative to its investigative process to help the parties reach a negotiated resolution. Information for filing complaints on Title II-related issues can be found on the Office for Civil Rights website. Individuals may also file a private lawsuit in Federal court.
The Family Educational Rights and Privacy Act (FERPA)
FERPA is a Federal law that protects the privacy of student education records. The law applies to all schools that receive funds under an applicable program of the U.S. Department of Education. FERPA gives parents certain rights with respect to their children's education records. Once a student reaches 18 years of age or begins attending a postsecondary institution, they become an “eligible student,” and all of the parent’s rights under FERPA transfer to the student. FERPA permits complaints to be filed at the federal level with the U.S. Department of Education.
Under FERPA, parents and eligible students have the right to a local level hearing to resolve disputes regarding the content of the student’s education record on the grounds that the information is inaccurate, misleading, or violates the student’s privacy rights. Parents and eligible students may also file a complaint with the U.S. Department of Education’s Student Privacy Policy Office to resolve issues related to their access to education records within required timelines, requests to amend or correct records they believe are inaccurate, misleading, or violate their privacy rights, and disclosure of the student’s education record to a third party they believe was improper. Information about FERPA and filing complaints on FERPA-related issues can be found on the U.S. Department of Education's Student Privacy Policy Office website.
Comparing Section 504 to IDEA
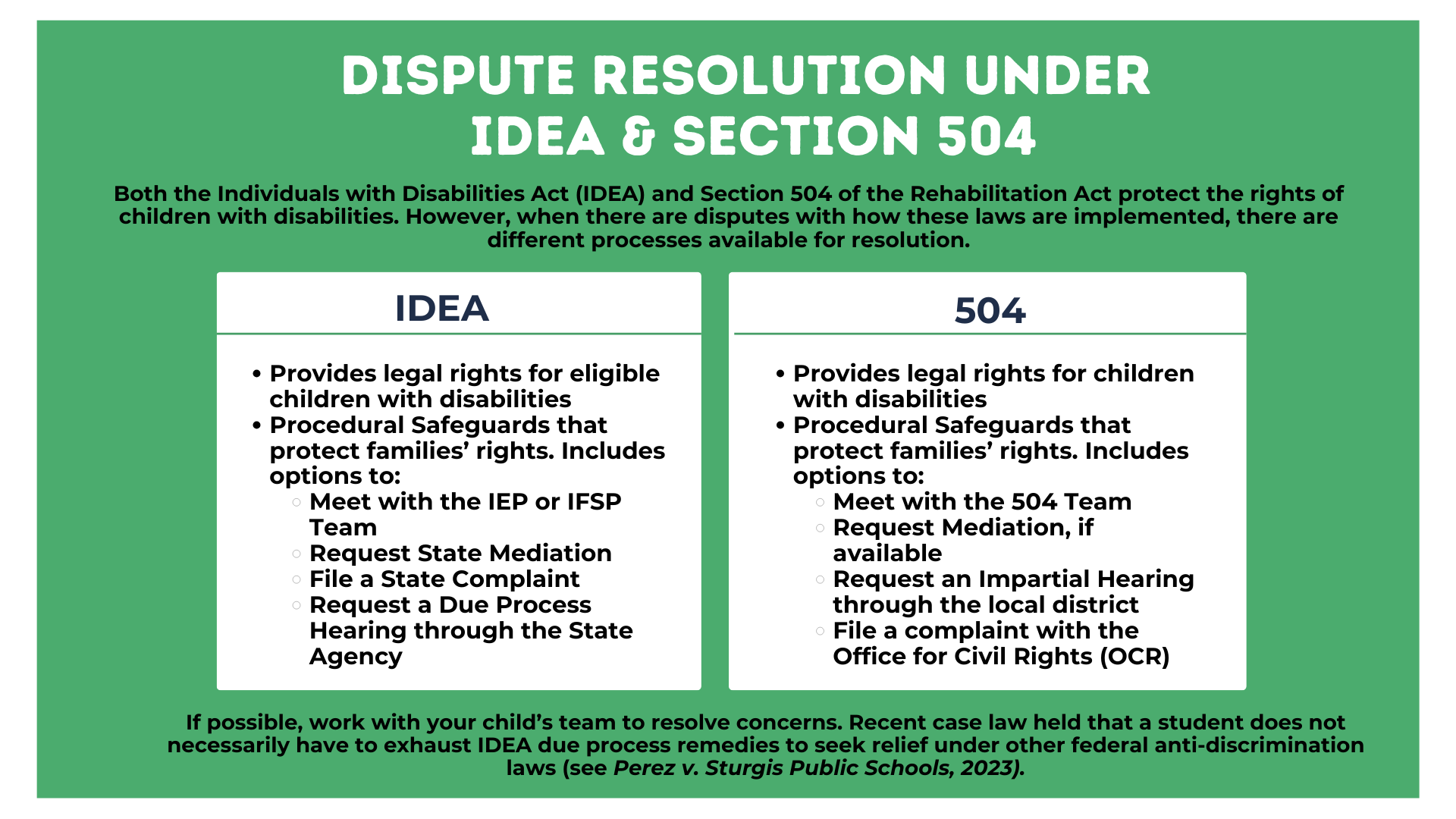
The dispute resolution options for disagreements regarding 504 plans and IEPs/IFSPs are covered under the two different federal laws. The dispute resolution rights available through the State agency under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) include the right to request mediation, to file a written State complaint, and to file a due process hearing request. Under Section 504 of the Rehabilitative Act of 1973, there is no legal requirement for mediation to be made available when there is a disagreement about a 504 plan, although many agencies offer this option. The resolution options required under Section 504 include the right to request an impartial hearing through the local educational agency or to file a complaint with the Office for Civil Rights (OCR).
CADRE's Information Guides for IDEA Dispute Resolution
CADRE developed these dispute resolution guides and process comparison charts to explain the different dispute resolution options available to families with children in early intervention (IDEA, Part C), and to parents and students in special education (IDEA, Part B). These guides and videos are available in multiple languages.
- IDEA Early Intervention Family Guides and Companion Videos: Family guides explain mediation, written state complaints, and due process complaints, along with companion videos, as well as a side-by-side comparison chart of dispute resolution options
- IDEA Dispute Resolution Parent Guides and Companion Videos: Parent guides explain facilitation, mediation, written state complaints, due process complaints, resolution meetings, and expedited due process complaints, along with companion videos, as well as a side-by-side comparison chart of dispute resolution options

